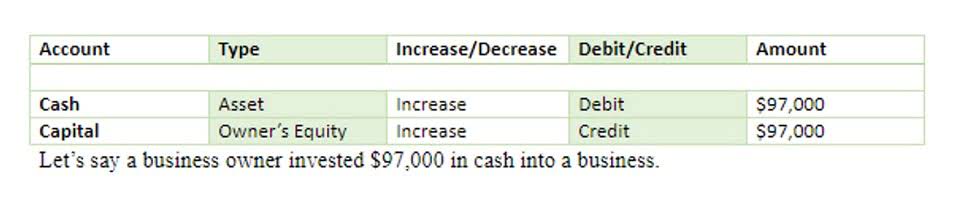
This document is essential as you learn how to calculate retained earnings and other equities. Retained earnings refer to the portion of a company’s profits that are reinvested back into the business, rather than being distributed to shareholders. Over time, retained earnings can have a significant impact retained earnings current or noncurrent on a company’s growth and profitability. When a company generates net income, it is typically recorded as a credit to the retained earnings account, increasing the balance. In contrast, when a company suffers a net loss or pays dividends, the retained earnings account is debited, reducing the balance.

Retained Earnings Formula
The first accounting option is to make no journal entry and disclose the amount of appropriation in the notes to the financial statement. The second option is to record a journal entry that transfers part of the unappropriated retained earnings into an Appropriated Retained Earnings account. To illustrate, assume that on March 3, Clay Corporation’s board of directors appropriates $12,000 of its retained earnings for future expansion. The company’s retained earnings account is first renamed as Unappropriated Retained Earnings.
Is Owners Equity and Retained Earnings the Same Thing?
- A company’s board of directors may designate a portion of a company’s retained earnings for a particular purpose such as future expansion, special projects, or as part of a company’s risk management plan.
- Create and send branded invoices, add fast payments, nudge late payers and track job expenses.
- That is the closing balance of the retained earnings account as in the previous accounting period.
- Overall, retained earnings include all profits or losses a company has made since the beginning.
- When money is borrowed by an individual or family from a bank or other lending institution, the loan is considered a personal or consumer loan.
- Retained earnings are the cumulative net earnings or profit of a company after paying dividends.
As the company loses ownership of its liquid assets in the form of cash dividends, it reduces the company’s asset value on the balance sheet, thereby impacting RE. Your current retained earnings are simply whatever you calculated during your last financial period. The same goes for the net profit/net loss, calculated by the month, quarter, year, or whatever your accounting period is. Whatever you paid shareholders in dividends for the period will reduce the amount shown in the statement of retained earnings. Negative retained earnings mean a negative balance of retained earnings as appearing on the balance sheet under stockholder’s equity.
Organization

These programs are designed to assist small businesses with creating financial statements, including retained earnings. Revenue, net profit, and retained earnings are terms frequently used on a company’s balance sheet, but it’s important to understand their differences. Alternatively, companies take the net income for the period to the retained earnings account first.
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
Stockholders’ equity is the amount of capital given to a business by its shareholders, plus donated capital and earnings generated by the operations of the business, minus any dividends issued. Retained earnings accumulate all profits and losses from when a company starts operating. However, it also deducts dividends from those amounts before reporting them on the balance sheet.
LO 4.6 Define, Explain, and Provide Examples of Current and Noncurrent Assets, Current and Noncurrent Liabilities
Many states restrict retained earnings by the cost of treasury stock, which prevents the legal capital of the stock from dropping below zero. Other restrictions are contractual, such as debt covenants and loan arrangements; these exist to protect creditors, often limiting the payment of dividends to maintain a minimum level of earned capital. On a sole proprietorship’s balance sheet and accounting equation, Owner’s Equity on one of three main components. Owner’s Equity is the owner’s investment in their own business minus the owner’s withdrawals from the business plus net income (or minus the net loss) since the business began. In a corporation, the earnings of a company are kept or retained and are not paid directly to owners.
- This concept is that no matter which of the entity options that you choose, the accounting process for all of them will be predicated on the accounting equation.
- They are typically highly illiquid, meaning these assets cannot easily be converted into cash.
- When the accounting period is finalized, the directors’ board opts to pay out $15,000 in dividends to its shareholders.
- Though cash dividends are the most common payout, remember that stock dividends are another option.
- Over the same duration, its stock price rose by $84 ($112 – $28) per share.
- Reinvestments from retained earnings help boost future earnings, while negative retained earnings typically indicate a need to reduce spending.
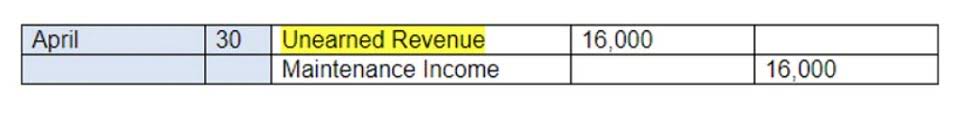
- Unearned revenue is money received or paid to a company for a product or service that has yet to be delivered or provided.

- The site is a tremendous resource for both school and investment-related research.
- Thus, stock dividends lead to the transfer of the amount from the retained earnings account to the common stock account.
- This process adds the profits or losses to the retained earnings balance.
- The table below reconciles the non-GAAP measure business segment operating profit with the most directly comparable GAAP financial measure, consolidated operating profit.
- Retained earnings (RE) are created as stockholder claims against the corporation owing to the fact that it has achieved profits.
- The correction involves changing the financial statement amounts to the amounts they would have been had no errors occurred, a process known as restatement.
- Depreciation expense would have been $1,000 higher if the correct depreciation had been recorded.